研究主題:低能量超音波造成大鼠動作腦區神經細胞調節活動之可行性評估
撰寫:學生邱千容
人耳能聽到的聲音大約介在20~20000 Hz之間,而高於此頻率範圍便稱為超音波。超音波是透過在不同介質(組織)間的傳遞速率以形成影像,其優點為快速且方便的使用方式以及價格相較其他檢驗工具較低廉,也因此超音波常做為最常被使用並應用的醫學影像工具之一。治療上常使用頻率較低的超音波而較高頻率的超音波則常使用於醫學診斷。在非侵入性神經調變研究方面,相較於顱外磁刺激術(repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation, rTMS)和跨顱直流電刺激(transcranial direct current stimulation, tDCS)只能在相對淺層、無法穿透深層腦區且具有個體差異化,新穎的經顱聚焦式超音波(Transcranial focused ultrasound, tFUS)技術利用曲面型壓電陶瓷使波聚焦在同一點,具有較高的空間解析度並可以更有效的到達人體腦部深處,且根據過往研究顯示tFUS的能量是抑制神經調變的重要參數之一。
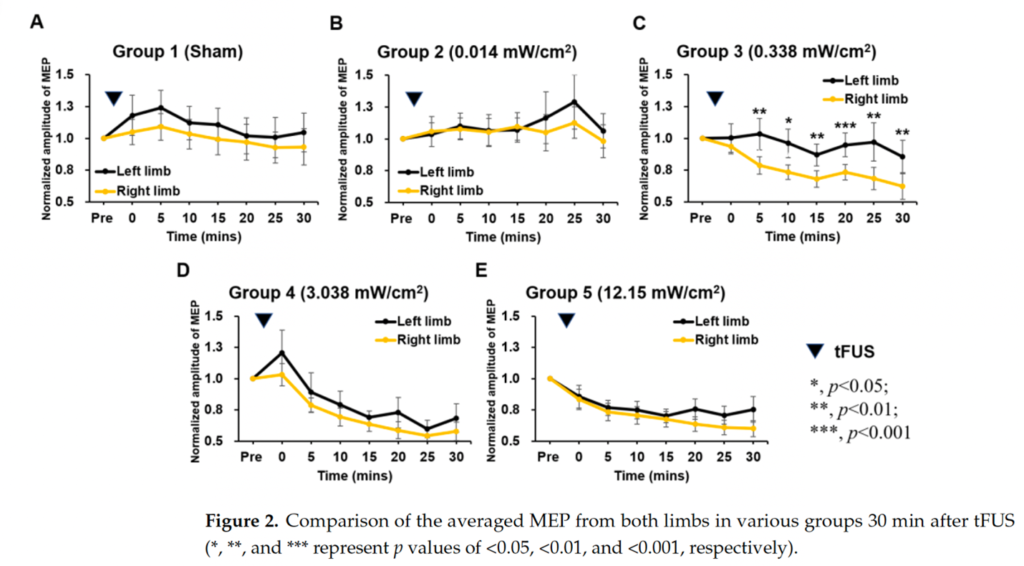
有別於過往研究發表在活體外使用低能量超音波誘導神經調變之影響,劉浩澧教授及其團隊在大鼠中使用不同量值的低能量超音波觀測刺激後一段時間內其運動神經電位(motor-evoked potentials, MEPs)之變化[1],並藉此定義出能有效使用tFUS刺激大鼠運動腦區誘導神經調變影響之最低值(約0.338 mW/cm2)。根據結果顯示,經過5分鐘的tFUS刺激後,可以降低運動神經活動約30分鐘,並且增進GABAergic神經的抑制性。該研究也指出在tFUS抑制神經調變中,抑制性神經元的活性是非常重要的指標之一。
雖然尚未有研究顯示在較長時間下tFUS對運動神經元活性和表現的影響以及其在人體上的應用;但在未來,tFUS具有高度發展性以及應用性,不但有機會作為診斷影像工具,還有可能作為治療神經系統性疾病。
Humans can hear sound with frequencies between 20 and 20,000 Hz, and the sound wave frequency that is above this interval is called ultrasound. The relatively low cost and rapid and convenient use of ultrasound make it one of the most commonly used and applied medical imaging tools. The lower-frequency ultrasound is often used in therapy, while higher-frequency is commonly used in medical diagnosis. Compared to techniques such as repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) and transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in non-invasive neuromodulation research, which are limited to relatively superficial layers and cannot penetrate deeper than the cortical layer of the brain and exhibit both within and between individuals, Transcranial Focused Ultrasound (tFUS) offers higher spatial resolution and can more effectively reach deep brain areas. Previous studies have shown that the intensity of tFUS is one of the important parameters for inhibiting neuromodulation.
In contrast to previous studies conducted in vitro using low-energy ultrasound to induce neuromodulation effects, Professor Hao-Li Liu and his team observed changes in motor-evoked potentials (MEPs) in rats after stimulation with different intensities of low-energy ultrasound over a period of time.[1] They defined the value (approximately 0.338 mW/cm2) as a threshold that can effectively induce neuromodulation effects in the motor cortex of rats using tFUS stimulation. According to the results, after 5 minutes of tFUS stimulation, motor neuron activity could be suppressed for about 30 minutes and it can also enhancing the inhibitory of GABAergic neurons. The study also indicated that the activity of inhibitory neurons is a crucial indicator in tFUS-induced neuromodulation.
Although no studies are showing the long-term effects of tFUS on motor neuron activity and the weak ultrasound’s application in humans, tFUS has high potential for development and application in the future. It may not only serve as a diagnostic imaging tool but also potentially be used in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders.
參考文獻
- Chu, P.-C., et al., Weak Ultrasound Contributes to Neuromodulatory Effects in the Rat Motor Cortex. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023. 24(3): p. 2578.