生醫電子所魏安祺教授實驗室
研究主題:粒線體毒性之大數據資料庫
撰寫:學生陳冠彬
粒線體是人體細胞中的能量工廠,負責細胞代謝以及製造三磷酸腺苷(ATP)。而粒線體對於細胞功能的調節佔有功不可沒的角色,當有外來藥物或是分子的影響時,粒線體有可能會受到損傷進而產生一些副作用。所以建構一個不同藥物或是分子對細胞產生影響時,相對應會產生哪些副作用的大數據資料庫就顯得非常重要,這不僅可以幫助醫生更好的去判斷病患的症狀也可以讓我們更近一步地去瞭解粒線體的工作原理。
粒線體的失常,往往跟心血管疾病、神經退化(阿茲罕默等)和癌症有相關聯,所以研究粒線體對於人類的健康可以說是至關重要。本所的魏老師致力於研究粒線體相關的研究,2021年魏老師在BMC Bioinformatics 發表了一篇研究,利用演算法將不同相關的開放資料庫統整在一起,建立了粒線體毒性的大數據資料庫MitoTox。MitoTox是一個提供毒物資料發現跟回報的開放平台,利用Python3植入多個不同網站的資料。目前MitoTox包含了1400個混合項目與其相對應的共有34000個不同的名詞。這所有的項目還連結了870多種粒線體毒性相關的蛋白質、蛋白質副產物跟RNA目標。這些毒化物根據他們的功能和毒物機制被分到8大類、225功能副分類和650個目標子集,而被記錄在其中的全部項目都有附上來源。
像這樣龐大的工程也歸功於現今資料科學的演進,而MitTox的建立不僅可以瞭解粒線體的機制(例如:細胞質中的電位改變和ATP的製造過程)更可以促進用藥安全以及毒性預防。如此高吞吐量的資料系統,提供了統計分析跟機器學習來研究粒線體的運作機制,也可以促進未來發現或預測更多的粒線體毒物及治療的方法。在文末魏老師也提到,MitoTox的初衷便是為了學習藥物是怎麼引發粒線體產生毒性以及其他副作用的影響。MitoTox建起了粒線體毒性跟副作用之間的橋樑,也為了未來的醫學預測提供了一條捷徑。
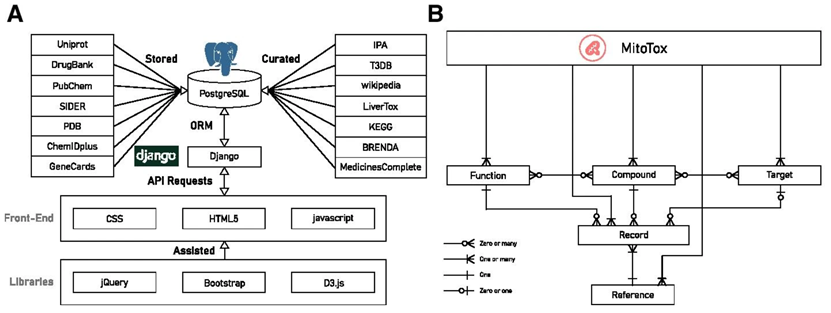
上圖為MitoTox的資料庫來源以及平台架構[1]
MitoTox database workflow and structure
The mitochondria are the energy factories of the human cells responsible for cellular metabolism and the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondria play a crucial role in regulating cellular functions, and they can be damaged and produce side effects when exposed to external drugs or molecules. Therefore, it is essential to construct a comprehensive database of big data that correlates different drugs or molecules with their corresponding side effects on cells. This not only helps doctors better diagnose patients’ symptoms but also allows us to further understand the working principles of mitochondria.
Mitochondrial dysfunction is often associated with cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders (such as Alzheimer’s), and cancer. Therefore, studying the impact of mitochondria on human health is of paramount importance. Dr. Wei from our institute is dedicated to mitochondrial research. In 2021, Dr. Wei published a study in BMC Bioinformatics, in which an algorithm was used to integrate various relevant open databases, creating a big data database called MitoTox, which focuses on mitochondrial toxicity. MitoTox is an open platform for discovering and reporting toxicological data, using Python3 to extract data from multiple websites. Currently, MitoTox includes 1,400 mixed items with 34,000 different terms associated with them. All these items are linked to over 870 mitochondrial toxicity-related proteins, protein by-products, and RNA targets. These toxins are categorized into eight major classes, 225 functional subcategories, and 650 target subsets, with their sources provided for all recorded items.
The establishment of a project of this magnitude is made possible by the evolution of data science today. The creation of MitoTox not only enhances our understanding of mitochondrial mechanisms (such as changes in cytoplasmic potential and ATP production processes) but also promotes drug safety and toxicity prevention. This high-throughput data system provides statistical analysis and machine learning tools to study the functioning mechanisms of mitochondria and facilitates the discovery and prediction of more mitochondrial toxins and treatment methods in the future. In conclusion, Dr. Wei also mentioned that the initial intention of MitoTox was to learn how drugs induce mitochondrial toxicity and other side effects. MitoTox serves as a bridge between mitochondrial toxicity and side effects, providing a shortcut for future medical predictions.
Ref:
[1] Y.-T. Lin, K.-H. Lin, C.-J. Huang, and A.-C. Wei, “MitoTox: a comprehensive mitochondrial toxicity database,” BMC Bioinformatics, vol. 22, no. 10, p. 369, 2021/07/15 2021, doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04285-3.