研究主題:乳鐵蛋白作為 COVID-19 的潛在預防和輔助治療
Lactoferrin as potential preventative and treatment for COVID-19.
撰寫:學生王馨
在2020 年,COVID-19 是一場已在全球蔓延的大流行病,並且還沒有成熟的抗病毒治療方法或疫苗。乳鐵蛋白是一種具有抗病毒和免疫調節特性的蛋白質,可能對類似於SARS-CoV-2(導致COVID-19的病毒)的病毒有效。它可以作為口服補充劑來治療或預防微生物感染,並被提議作為COVID-19的潛在預防和輔助治療。孫教授和其團隊正在研究乳鐵蛋白的抗病毒特性和免疫調節機制及其針對SARS-CoV-2的潛在用途。
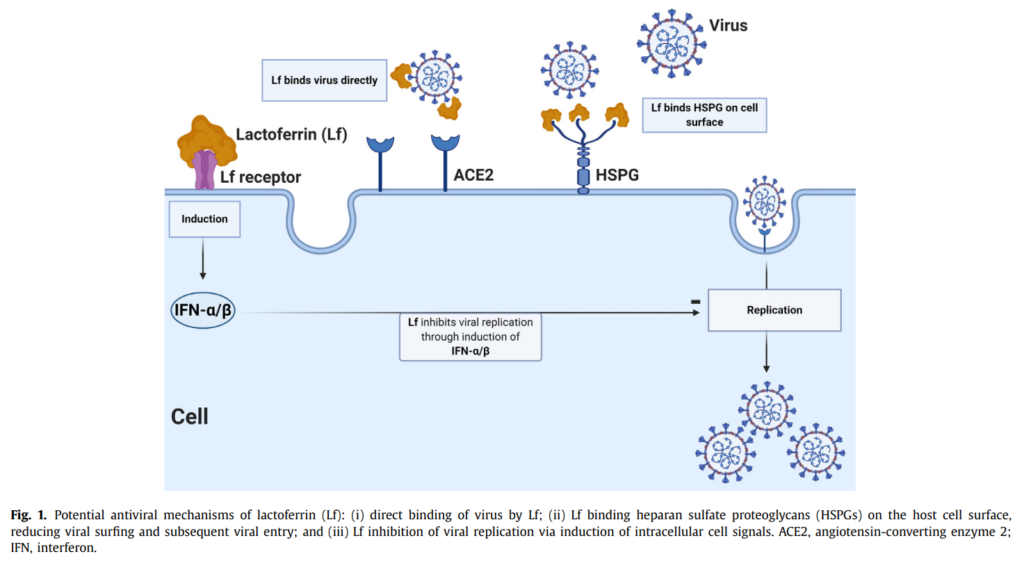
乳鐵蛋白可以透過與細胞表面分子或病毒顆粒或兩者結合來抑制病毒進入。它還被證明可以在病毒進入細胞後抑制病毒複製,並對免疫細胞發揮間接抗病毒作用。乳鐵蛋白已在人類口服補充劑研究中進行了研究,並被發現可以降低感冒和類似感冒症狀的發生率,並改善輪狀病毒性腸胃炎。它也被證明可以降低 HCV病毒效價並改善 HCV 患者的持續病毒學反應。它還具有通過調節涉及細胞因子、趨化因子和細胞表面受體的信號通路來維持免疫和生理穩態並限制組織損傷的能力。在一項使用脂多醣 (LPS) 注射模型重現由細菌引起的病理生理變化的研究中,乳鐵蛋白治療以劑量依賴的方式降低膿毒症小鼠的死亡率。在LPS注射前,單劑量乳鐵蛋白將小鼠死亡率降低至 16.7%,而對照組83.3%。
乳鐵蛋白已被證明可透過與小鼠和人類冠狀病毒中的宿主細胞表面硫酸乙酰肝素蛋白多醣 (HSPG) 結合來抑制病毒進入。因此研究團隊認為,乳鐵蛋白可能可以透過與 HSPG 結合並促進血管緊張素轉換酶 2 (ACE2) 等入口受體來抑制 SARS-CoV-2病毒進入宿主細胞。最近的一項研究發現,每天服用四到六次含鋅的脂質體牛乳鐵蛋白補充劑,持續10天,可使75名有症狀的SARS-CoV-2 陽性患者在4-5天內100%康復。乳鐵蛋白還被認為具有免疫調節和抗發炎特性,可能有助於減少COVID-19嚴重病例的發炎和細胞因子風暴。
In 2020, COVID-19 was a pandemic that had spread globally and had no established antiviral treatments or vaccines. Lactoferrin (Lf) is a protein with antiviral and immunomodulatory properties that may be effective against viruses similar to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It may be taken as an oral supplement to potentially treat or prevent microbial infections and is proposed as a potential preventative and adjunct treatment for COVID-19. The antiviral properties and immunomodulatory mechanisms of Lf were examined by Prof. Sun and his team in relation to its potential use against SARS-CoV-2.
Lf can inhibit viral entry by binding to cell surface molecules or viral particles, or both. It has also been shown to suppress virus replication after the virus enters the cell, and to exert an indirect antiviral effect on immune cells. Lf has been studied in human oral supplementation studies and has been found to reduce the incidence of colds and cold-like symptoms and to ameliorate rotaviral gastroenteritis. It has also been shown to decrease HCV viral titres and improve sustained virological response in HCV patients. It also has the ability to maintain immune and physiological homeostasis and limit tissue damage by modulating signaling pathways involving cytokines, chemokines, and cell surface receptors. In a study using a lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection model to reproduce the pathophysiological changes caused by bacteria, Lf treatment was found to reduce the mortality of mice with sepsis in a dose-dependent manner. A single dose of lactoferrin before LPS injection reduced the mortality of mice to 16.7% compared to 83.3% in controls.
Lf has been shown to inhibit viral entry by binding to host cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) in murine and human coronaviruses. The research team believed that Lf may also be able to inhibit the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into host cells by binding to HSPGs and facilitating entry receptors such as angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). A recent study found that a liposomal bovine Lf supplement administered at four to six doses per day for 10 days with zinc resulted in 100% recovery of 75 symptomatic SARS-CoV-2-positive patients within 4-5 days. Lf is also believed to have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties that may be useful in reducing inflammation and cytokine storms in severe cases of COVID-19.